Rust 交叉编译与条件编译总结
原文¶
https://www.jianshu.com/p/0e4251bc10eb
主体项目编译前的操作(build.rs)¶
build.rs可实现本项目编译前的额外操作,比如代码生成、调用cmake/clang/gcc/ndk-build等编译所依赖的C/C++库、读取C/C++头文件生成FFI文件给Rust项目使用等等,相当于Rust写的shell脚本。 为了让编译过程更可控,通常输出日志表示通过了某一阶段,或遇到什么错误,Cargo支持build.rs编译时输出不同类型的语句,比如warning、error等,比如:
目前没找到输出info级别日志的办法,经实践println!("cargo:info={:?}, some_status);无法在控制台输出信息。
build.rs拉取git submodule¶
以下代码摘自glsl-to-spirv。
use std::process::Command;
// Try to initialize submodules. Don't care if it fails, since this code also runs for
// the crates.io package.
let _ = Command::new("git")
.arg("submodule")
.arg("update")
.arg("--init")
.status();
Cargo调用clang编译所依赖的第三方C/C++库¶
目前我看到比较完整的参考是官方的libstd/build.rs,编译我们业务所需的第三方库的命令几乎都可以从那找到“灵感”,下面贴出核心代码段镇宅,关键操作是build_libbacktrace(),通过cc::Build实例把需要编译的C/C++代码声明起来,理论上支持正则匹配文件名与路径 。
#![deny(warnings)]
extern crate build_helper;
extern crate cc;
use build_helper::native_lib_boilerplate;
use std::env;
use std::fs::File;
fn main() {
let target = env::var("TARGET").expect("TARGET was not set");
if cfg!(feature = "backtrace") &&
!target.contains("cloudabi")
// ... 更多条件
{
let _ = build_libbacktrace(&target);
}
if target.contains("linux") {
// ... 一系列操作系统判断及println!
}
}
fn build_libbacktrace(target: &str) -> Result<(), ()> {
let native = native_lib_boilerplate("libbacktrace", "libbacktrace", "backtrace", "")?;
let mut build = cc::Build::new();
build
.flag("-fvisibility=hidden")
.include("../libbacktrace")
.include(&native.out_dir)
.out_dir(&native.out_dir)
.warnings(false)
.file("../libbacktrace/alloc.c")
.file("../libbacktrace/backtrace.c")
// ...一堆.c文件
let any_debug = env::var("RUSTC_DEBUGINFO").unwrap_or_default() == "true" ||
env::var("RUSTC_DEBUGINFO_LINES").unwrap_or_default() == "true";
build.debug(any_debug);
if target.contains("darwin") {
build.file("../libbacktrace/macho.c");
} else if target.contains("windows") {
build.file("../libbacktrace/pecoff.c");
} else {
build.file("../libbacktrace/elf.c");
let pointer_width = env::var("CARGO_CFG_TARGET_POINTER_WIDTH").unwrap();
if pointer_width == "64" {
build.define("BACKTRACE_ELF_SIZE", "64");
} else {
build.define("BACKTRACE_ELF_SIZE", "32");
}
}
File::create(native.out_dir.join("backtrace-supported.h")).unwrap();
build.define("BACKTRACE_SUPPORTED", "1");
build.define("BACKTRACE_USES_MALLOC", "1");
build.define("BACKTRACE_SUPPORTS_THREADS", "0");
build.define("BACKTRACE_SUPPORTS_DATA", "0");
File::create(native.out_dir.join("config.h")).unwrap();
if !target.contains("apple-ios") &&
!target.contains("solaris") &&
!target.contains("redox") &&
!target.contains("android") &&
!target.contains("haiku") {
build.define("HAVE_DL_ITERATE_PHDR", "1");
}
build.define("_GNU_SOURCE", "1");
build.define("_LARGE_FILES", "1");
build.compile("backtrace");
Ok(())
}
Cargo调用ndk-build编译第三方C/C++库¶
以下代码参考自rustdroid-native
use std::{env, path::PathBuf, process};
fn main() {
establish_ndk();
establish_ndk_toolchain();
}
fn establish_ndk() {
match find_ndk_path() {
None => println!("cargo:warning=NDK path not found"),
Some(path) => println!("cargo:warning=NDK path found at {}", path.to_string_lossy()),
};
}
fn establish_ndk_toolchain() {
match find_ndk_toolchain_path() {
None => println!("cargo:warning=NDK_TOOLCHAIN path not found"),
Some(path) => println!(
"cargo:warning=NDK_TOOLCHAIN path found at {}",
path.to_string_lossy()
),
};
}
fn command_which_ndk_build_path() -> Option<PathBuf> {
let mut cmd = process::Command::new("sh"); // mut due to API limitation
cmd.arg("-c").arg("which ndk-build");
match cmd.output() {
Err(e) => {
println!(
"cargo:warning=Error executing process command <{:?}>: {}",
cmd, e
);
None
}
Ok(o) => match String::from_utf8(o.stdout) {
Err(e) => {
println!("cargo:warning=Error parsing command output as UTF-8: {}", e);
None
}
Ok(s) => PathBuf::from(&s)
.parent()
.and_then(|p| Some(p.to_path_buf())),
},
}
}
fn path_from_string(pathname: &str) -> Option<PathBuf> {
// TODO: @@@ FUTURE RUST FEATURE
//Some(PathBuf::from(pathname)).filter(|p| p.exists())
let path = PathBuf::from(&pathname);
if path.exists() {
Some(path)
} else {
None
}
}
fn path_from_env_var(varname: &'static str) -> Option<PathBuf> {
match env::var(varname) {
Ok(s) => path_from_string(&s),
Err(_) => None,
}
}
fn path_with_ndk_build(path: &PathBuf) -> Option<PathBuf> {
// TODO: @@@ FUTURE RUST FEATURE
//path.filter(|p| p.join("ndk-build").exists())
if path.join("ndk-build").exists() {
Some(path.clone())
} else {
None
}
}
fn path_with_ndk_bundle_ndk_build(path: &PathBuf) -> Option<PathBuf> {
path_with_ndk_build(&path.join("ndk-bundle"))
}
fn path_with_ndk_build_from_env_var(varname: &'static str) -> Option<PathBuf> {
path_from_env_var(&varname).and_then(|p| path_with_ndk_build(&p))
}
fn path_with_ndk_bundle_ndk_build_from_env_var(varname: &'static str) -> Option<PathBuf> {
path_from_env_var(&varname).and_then(|p| path_with_ndk_bundle_ndk_build(&p))
}
fn find_ndk_path_from_ndk_env_vars() -> Option<PathBuf> {
// TODO: @@@ REFACTOR INTO ITERATION OF COLLECTION
path_with_ndk_build_from_env_var("ANDROID_NDK_HOME").or_else(|| {
path_with_ndk_build_from_env_var("ANDROID_NDK_ROOT").or_else(|| {
path_with_ndk_build_from_env_var("NDK_HOME").or_else(|| {
path_with_ndk_build_from_env_var("NDK_ROOT") // NVIDIA CodeWorks
.or_else(|| path_with_ndk_build_from_env_var("NDKROOT"))
})
})
}) // NVIDIA CodeWorks
}
fn find_ndk_path_from_sdk_env_vars() -> Option<PathBuf> {
// TODO: @@@ REFACTOR INTO ITERATION OF COLLECTION
path_with_ndk_bundle_ndk_build_from_env_var("ANDROID_SDK_HOME")
.or_else(|| path_with_ndk_bundle_ndk_build_from_env_var("ANDROID_SDK_ROOT"))
.or_else(|| path_with_ndk_bundle_ndk_build_from_env_var("ANDROID_HOME"))
}
fn find_ndk_path_from_env_vars() -> Option<PathBuf> {
find_ndk_path_from_ndk_env_vars().or_else(|| find_ndk_path_from_sdk_env_vars())
}
fn find_ndk_version_build_path(path: &PathBuf) -> Option<PathBuf> {
//println!("cargo:warning=find_ndk_version_build_path() pathname: {:?}", pathname);
if let Ok(iter) = path.read_dir() {
for entry in iter {
if let Ok(entry) = entry {
let path = entry.path();
//println!("cargo:warning=searching path: {:?}", path);
if path.join("ndk-build").exists() {
return Some(path);
}
}
}
}
None
}
fn find_ndk_path_from_known_installations() -> Option<PathBuf> {
env::home_dir().and_then(|home| {
path_with_ndk_bundle_ndk_build(
// Android Studio on GNU/Linux
&home.join(".android").join("sdk"),
)
.or_else(|| {
path_with_ndk_bundle_ndk_build(
// Android Studio on macOS
&home.join("Library").join("Android").join("sdk"),
)
})
.or_else(|| {
find_ndk_version_build_path(
// NVIDIA CodeWorks
&home.join("NVPACK"),
)
})
})
}
fn find_ndk_path() -> Option<PathBuf> {
command_which_ndk_build_path()
.or_else(|| find_ndk_path_from_env_vars())
.or_else(|| find_ndk_path_from_known_installations())
}
fn find_ndk_toolchain_path() -> Option<PathBuf> {
path_from_env_var("NDK_TOOLCHAIN")
}
图形开源项目build.rs参考编译脚本¶
Cargo编译glslang¶
缺点:没对应到最新的glslang项目。优点:使用文件后缀匹配需要编译的文件,避免硬编码。八卦:此项目作者是Google员工,他还开发了cargo-lipo项目,极大地方便了Rust编译iOS库,刚接触Rust时我啥都不懂,还给他提了一个错误的issue,导致Josh和他讨论了一段时间。
glsl-to-spirv 直接用glslang自带CMakeList.txt,此方案对于快速迭代且持续维护的开源项目是很好的选择,降低build.rs编写、维护成本。
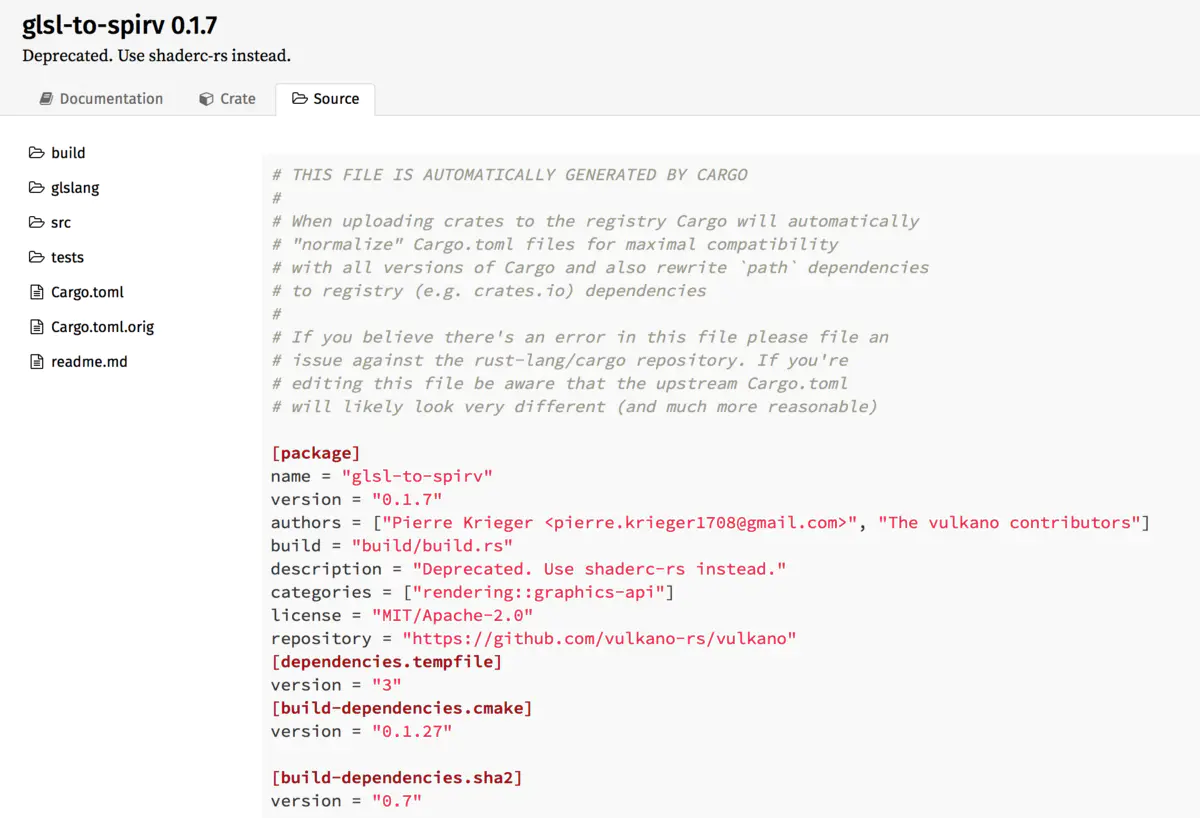
Cargo编译SPIRV-Cross¶
缺点:硬编码参与编译的文件列表。优点:这是Josh的项目,工程组织上比前面glslang-sys项目更成熟,很值得参考。
Cargo编译Metal Shader文件到.metallib¶
编译Metal的.shader文件为.metallib,避免运行时编译,提高性能。值得参考的地方是,如何在build.rs中调用XCode编译工具链。
通过build.rs创建目录¶
use std::fs;
fn main() {
fs::create_dir_all("./dir1/dir2/dir3"); // 1
fs::create_dir_all("./../lib"); // 2
}
//1在build.rs同级目录中创建出dir1/dir2/dir3所需的所有目录。比如,dir1、dir2都不存在,则fs::create_dir_all()会自动创建它们,然后创建出dir3。//2在build.rs上级目录创建lib目录。
结论:fs::create_dir_all()要注意路径的区别。
参考:How to check if a directory exists and create a new one if it doesn't in Rust?
项目编译后的操作¶
比如目前Rust项目还不支持直接编译成iOS/macOS支持的.framework,我们还得用脚本把.a和.h打包进.framework给客户,如果有编译后操作支持就非常棒了,遗憾的是,目前还没有,经 @我傻逼我自豪(茶包) 兄提醒,这事已经在讨论了cargo/issue。
条件编译¶
所有的条件编译都由通过cfg配置实现,cfg支持any、all、not等逻辑谓词组合。
基本用法¶
在Cargo.toml中添加[features]段,然后列举需要组合的feature名,大体上相当于gcc -条件1 -条件2 -条件3 ...。
[features]
default = []
metal = ["gfx-backend-metal"]
vulkan = ["gfx-backend-vulkan"]
dx12 = ["gfx-backend-dx12"]
mod级别条件编译¶
实现示例,参考gl-rs/gl_generator/lib.rs
#[cfg(feature = "unstable_generator_utils")]
pub mod generators;
#[cfg(not(feature = "unstable_generator_utils"))]
mod generators;
编译特定CPU架构¶
指定target_arch + CPU架构名称字符串,如#[cfg(target_arch= "x86")],#[cfg(any(target_arch = "arm", target_arch = "x86"))]。
#[cfg(any(target_arch = "arm", target_arch = "x86"))]
mod arch {
use os::raw::{c_uint, c_uchar, c_ulonglong, c_longlong, c_ulong};
use os::unix::raw::{uid_t, gid_t};
#[stable(feature = "raw_ext", since = "1.1.0")]
pub type dev_t = u64;
#[stable(feature = "raw_ext", since = "1.1.0")]
pub type mode_t = u32;
#[stable(feature = "raw_ext", since = "1.1.0")]
pub type blkcnt_t = u64;
#[stable(feature = "raw_ext", since = "1.1.0")]
pub type blksize_t = u64;
#[stable(feature = "raw_ext", since = "1.1.0")]
pub type ino_t = u64;
#[stable(feature = "raw_ext", since = "1.1.0")]
pub type nlink_t = u64;
#[stable(feature = "raw_ext", since = "1.1.0")]
pub type off_t = u64;
#[stable(feature = "raw_ext", since = "1.1.0")]
pub type time_t = i64;
#[doc(include = "os/raw/char.md")]
#[cfg(any(all(target_os = "linux", any(target_arch = "aarch64",
target_arch = "arm",
target_arch = "powerpc",
target_arch = "powerpc64",
target_arch = "s390x")),
iOS/Android/macOS/Windows跨平台编译示例¶
[target.'cfg(any(target_os = "macos", all(target_os = "ios", target_arch = "aarch64")))'.dependencies.gfx-backend-metal]
git = "https://github.com/gfx-rs/gfx"
version = "0.1"
optional = true
[target.'cfg(target_os = "android")'.dependencies.gfx-backend-vulkan]
git = "https://github.com/gfx-rs/gfx"
version = "0.1"
optional = true
[target.'cfg(windows)'.dependencies.gfx-backend-dx12]
git = "https://github.com/gfx-rs/gfx"
version = "0.1"
optional = true
编译时指定例如cargo build --features metal --target aarch64-apple-ios --release可编译relase版64位iOS静态库,同时将feature为gfx-backend-metal的代码打包进来(需要配置前面的features段)。
同理,cargo build --features vulkan --target aarch64-linux-android --release可编译relase版64位Android静态库,同时将feature为gfx-backend-vulkan(需要配置前面的features段)。
编译成指定类型二进制包(.a/.so/.r)¶
目前还没找到支持编译出macOS/iOS支持的.framework办法。
在Cargo.toml中添加[lib]段,
-
name表示输出的库名,最终输出文件名为lib+name.a或lib+name.so,比如libportability.so。 -
crate-type
表示输出的二进制包类型,比如
staticlib= .a iOS只认Rust输出.a,Android可以.a和.so,配置成["staticlib", "cdylib"]在用cargo-lipo时会出警告不支持cdylib,忽略即可。cdylib= .sorlib= 给Rust用的静态库-
dylib= 给Rust用的动态库 -
path表示库项目的入口文件,通常是src/lib.rs,如果改动了这一位置,可通过path = 新位置实现,比如:
[lib] name = "portability" crate-type = ["staticlib", "cdylib"] path = "src/ios/lib.rs"
## SDK开发的“售后服务”
提供.a/.so给业务团队,这一过程可能会有人为失误导致大家对接失败,下面介绍些我们使用的小技巧。
### 读取.a静态库的iOS版本
在macOS terminal执行如下命令,用`/`查找`VERSION`。
otool -lv xyz.a | less
参考:[check-ios-deployment-target-of-a-static-library](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/30466062/check-ios-deployment-target-of-a-static-library)
### nm查看导出符号
有时编码疏忽导致没给需要导出的C接口添加`#[no_mangle]`和`extern`等修饰,或者使用了不合理的优化attribute导致符号被优化掉,此时业务链接我们的库就会失败,因此,交付二进制包前用nm确认符号表是合格的工程师习惯。参考:[How do I list the symbols in a .so file](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/34732/how-do-i-list-the-symbols-in-a-so-file)。以下为macOS示例代码。
#### nm查看.so导出符号
nm -D ./target/release/libportability.so | grep fun_call_exported_to_c 0000000000003190 T fun_call_exported_to_c
nm -g ./target/release/libportability.a | grep glActiveTexture 000000000000190c T _glActiveTexture
## Rust导出C接口的正确姿势
> The Rust philosophy is to prefer explicit over implicit.
> **Rust will only export symbols that are publicly accessible from the root crate. This makes it very easy to inspect the public interface of a crate without crawling through all files: just follow the pub from the root.**
> In your case, the symbol rle_new is publicly accessible to anyone having access to the rle module (such as sibling modules), but the rle module itself is not publicly accessible in the root crate.
>
> The simplest solution is to selectively export this symbol:
>
>
>
>
> ```pub use rle::rle_new;```
>
>
> https://stackoverflow.com/questions/40131838/function-is-marked-no-mangle-but-not-exported
因此,对于在非lib.rs中标识`#[no_mangle]`的函数,如果忘了在lib.rs中pub use它,打包成C库或rlib还是找不到且出现如下编译警告。**解决办法就是在lib.rs中要么`pub use 模块::\*`或`pub use 模块::{符号名1, 符号名2}`**。
warning: function is marked #[no_mangle], but not exported
--> src/portability/gl_es/src/c_abi/mod.rs:785:1
|
785 | / pub extern "C" fn glViewport(x: GLint, y: GLint, width: GLsizei, height: GLsizei) {
786 | | unimplemented!()
787 | | }
| |_^
|
= help: try exporting the item with a `pub use` statement
### 查看本机rust编译器可编译的系统列表
rustc --print target-list